Complex numbers
Numbers that have a real number component and an imaginary number component (which is a real number multiplied by the square root of -1).
Counting/Natural/Whole numbers
The counting numbers start at 1 and increase by 1 (1, 2, 3, 4,...). The whole numbers include 0 and the natural numbers sometimes do include 0 and sometimes don't.
Dependent variable
The dependent variable, often labeled y in an x, y scheme, is the variable that gets its value from an equation's operation(s) on the independent variable.
Domain
The domain is a list of all the values of a function that are allowable. For instance, in the function 1 / x, x cannot equal 0 (because dividing by 0 makes a fraction undefined. Think of taking a pizza and cutting it into 0 slices... but even having the pizza means that there is at least one slice. And so we'd have to get rid of the pizza... and having a fraction talking about a pizza that is completely non-existent makes the whole fraction become undefined.
FOIL
This is the method used to multiply two binomials together, such as
- First terms - in our case that's

- Outside terms - in our case that's

- Inside terms - in our case that's

- Last terms - in our case that's
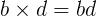
All this gives:
Imaginary numbers
Whole numbers multiplied by the square root of -1, which is symbolized with the letter i.
Independent variable
The independent variable, often labeled x in an x, y scheme, is the variable that is acted upon by an equation and which results in a resulting value.Integer numbers
The positive and negative whole numbers (...,-3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3,...)
Irrational numbers
Numbers along a number line that can't be expressed as the fraction of two integers (ex. pi).
Line equation, Double intercept form
An equation in the form of
Line equation, Point-slope form
An equation in the form of, where m is the slope and
is a point on the line
Line equation, Slope-intercept form
An equation in the form of, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept
Line equation, Standard form
An equation in the form ofwhere A, B, and C are all integers and A is positive.
Counting/Natural/Whole numbers
The counting numbers start at 1 and increase by 1 (1, 2, 3, 4,...). The whole numbers include 0 and the natural numbers sometimes do include 0 and sometimes don't.
Order of Operations (PEMDAS)
This is the order in which we work expressions/equations:
- P = Parentheses (also known as Brackets)
- E = Exponentials
- M = Multiplication (same weight as Division)
- D = Division (same weight as Multiplication)
- A = Addition (same weight as Subtraction)
- S = Subtraction (same weight as Addition)
Quadratic Formula
where the trinomial is in the form ax^2 + bx + c
Range
Rational numbers
Real numbers
Counting/Natural/Whole numbers
The range is the list of all the values that arise from the equation working on the domain. For example, in the equation y = |x| (y equals the absolute value of x), y will never be negative (because the absolute value operation takes whatever is inside and makes it positive). Therefore, the range is y >= 0.
Rational numbers
Numbers that can be expressed as the fraction of two integers.
Real numbers
All the numbers along a number line and is comprised of both Rational and Irrational numbers.
Counting/Natural/Whole numbers
The counting numbers start at 1 and increase by 1 (1, 2, 3, 4,...). The whole numbers include 0 and the natural numbers sometimes do include 0 and sometimes don't.




No comments:
Post a Comment
Hey there - thanks for your comment! It's always a pleasure to converse with someone who's interested in math.
As part of the security for this page, I've turned moderation on - so I have to look at your comment before it goes on the page (which will prevent horrible people trying to say and do horrible things here). I'll have your comment posted shortly and far more importantly a response in short order after that.
Feel free to share this page if you find it at all helpful!
Parz